目的 探讨丁苯酞注射液治疗急性缺血性脑卒中对患者神经功能及认知的影响。方法 选取2016-02—2017-11郑州市急救网络医院收治的急性缺血性脑卒中患者106例,按入院顺序分为对照组及研究组各53例。对照组患者进行常规抗血栓及其他对症支持治疗,研究组患者在对照组的基础上联合丁苯酞注射液治疗,2组均连续治疗2周,随访至治疗后3个月。检测并比较2组治疗前后神经功能及认知改善情况。结果 研究组神经功能改善总有效率86.79%,显著高于对照组的67.92%(χ2=5.386,P=0.020);与治疗前比较,治疗后3 d~3个月2组NIHSS评分均呈逐渐降低趋势,MMSE评分及MoCA评分均呈逐渐升高趋势(P<0.01),且治疗后1、3个月研究组NIHSS评分显著低于对照组(P<0.05),治疗后3 d、7 d、1个月及3个月研究组MMSE评分显著高于对照组(P<0.05或0.01);治疗后7 d、1个月及3个月研究组MoCA评分均显著高于对照组(P<0.05或0.01)。治疗期间2组均未见严重不良反应。结论 丁苯酞注射液可有效改善急性缺血性脑卒中患者神经功能及认知功能,具有良好的安全性,疗效显著。
丁苯酞注射液对急性缺血性脑卒中患者神经功能及认知的影响
赵 琰1) 李 华2)△ 王景涛3)
1)郑州市紧急医疗救援中心急救管理科,河南郑州 450047 2)河南省中医院急诊科,河南郑州 450002 3)郑州大学第一附属医院神经内科,河南郑州 450052
基金项目:河南省中医药科学研究专项(编号:2017ZY2134)
作者简介:赵琰,Email:zz120zy@163.com
△通信作者:李华,Email:lihua771203@163.com
【摘要】 目的 探讨丁苯酞注射液治疗急性缺血性脑卒中对患者神经功能及认知的影响。方法 选取2016-02—2017-11郑州市急救网络医院收治的急性缺血性脑卒中患者106例,按入院顺序分为对照组及研究组各53例。对照组患者进行常规抗血栓及其他对症支持治疗,研究组患者在对照组的基础上联合丁苯酞注射液治疗,2组均连续治疗2周,随访至治疗后3个月。检测并比较2组治疗前后神经功能及认知改善情况。结果 研究组神经功能改善总有效率86.79%,显著高于对照组的67.92%(χ2=5.386,P=0.020);与治疗前比较,治疗后3 d~3个月2组NIHSS评分均呈逐渐降低趋势,MMSE评分及MoCA评分均呈逐渐升高趋势(P<0.01),且治疗后1、3个月研究组NIHSS评分显著低于对照组(P<0.05),治疗后3 d、7 d、1个月及3个月研究组MMSE评分显著高于对照组(P<0.05或0.01);治疗后7 d、1个月及3个月研究组MoCA评分均显著高于对照组(P<0.05或0.01)。治疗期间2组均未见严重不良反应。结论 丁苯酞注射液可有效改善急性缺血性脑卒中患者神经功能及认知功能,具有良好的安全性,疗效显著。
【关键词】 急性缺血性脑卒中;急性脑梗死;丁苯酞注射液;神经功能;认知
【中图分类号】 R743.33 【文献标识码】 A 【文章编号】 1673-5110(2018)24-2708-06 DOI:10.12083/SYSJ.2018.24.565
Effect of butylphthalide injection on the nerve function and cognition of acute ischemic stroke patients
ZHAO Yan1),LI Hua2),WANG Jingtao3)
1)Department of Emergency Management,Zhengzhou Emergency Medical Rescue Center,Zhengzhou 450047,China;2)Department of Emergency,Henan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450002,China;3)Department of Neurology,the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University,Zhengzhou 450052,China
【Abstract】 Objective To explore the effect of butylphthalide injection on the nerve function and cognition of acute ischemic stroke patients.Methods 106 cases acute ischemic stroke patients treated in First Aid Network Hospital of Zhengzhou City from Feb.2016 to Nov.2017 were selected and divided into control group and study group according to admission order,53 cases were for each group.Patients in control group were treated with conventional antithromboembolism and other symptomatic support treatments,patients in study group were treated with butylphthalide injection on the basis of control group,and were treated for 2 weeks continuously and followed-up until 3-month after treatment.The improvement of nerve function and cognition in 2 groups were detected and compared.Results he total effective rate of nerve function improvement in study group was 86.79%,which was higher than that 67.92% in the control group (χ2=5.386,P=0.020);compared with before treatment,the NIHSS scores from 3-day to 3-month after treatment in 2 groups decreased gradually,the MMSE scores and MoCA scores in 2 groups increased gradually (P<0.01),and the NIHSS scores in study were lower than those in control group 1-month,3-month after treatment (P<0.05),the MMSE scores in study group were higher than those in control group 3-day,7-day,1-month and 3-month after treatment (P<0.05 or P<0.01);the MoCA scores in study group were higher than those in control group 7-day,1-month and 3-month after treatment (P<0.05 or P<0.01).There was no severe adverse reactions occurred during the treatment in 2 groups.Conclusion Butylphthalide injection can improve the nerve function and cognition function of acute ischemic stroke patients effectively,and which has good security.
【Key words】 Acute ischemic stroke;Acute cerebral infarction;Butyl phthalate injection;Nerve function;Cognition
急性缺血性脑卒中具有较高的致残、致死率,通常是由脑部供血血管狭窄或闭塞导致脑组织供血不足,发生脑组织坏死,导致脑部神经损伤[1-5]。目前主张对急性缺血性脑卒中进行早期诊断、早期治疗及预防,以常规抗血栓治疗及相关对症支持治疗为主[6-15],但疗效并不理想。丁苯酞注射液是中国自主研制的一种新型神经保护剂。研究[16-22]报道,其可作用于脑梗死发病的多个环节,有助于提高患者脑血流量,改善患者认知。本研究探讨丁苯酞注射液治疗急性缺血性脑卒中对患者神经功能、认知的影响。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取2016-02—2017-11郑州市急救网络医院院前接诊的106例急性缺血性脑卒中患者,入院后均经颅脑CT或MRI检测确诊,并符合全国脑血管病学术会议制定的相关诊断标准。纳入标准:年龄30~65岁;首次发病,且发病至入院时间<24 h;伴局灶性神经功能缺损,表现为面神经瘫痪;美国国立卫生研究院卒中量表(NHISS)评分2~12分;意识清楚可配合简易精神状态量表(MMSE)及蒙特利尔认知评估量表(MoCA)检测;患者及其家属对本研究知情同意。排除标准:伴严重视听障碍等原发性疾病,不能配合研究者;伴全身系统性严重疾病者;对本研究所用药物过敏者;入院前行急诊溶栓或介入治疗者;发病前服用叶酸、钴胺素者。2组基线资料无显著性差异(P>0.05),具有可比性。见表1。本研究已通过院医学伦理委员会审批。
1.2 方法 2组入院后均给予常规抗血小板聚集治疗,同时给予活血化瘀、降压、调脂、控制血糖等对症支持治疗。研究组加用丁苯酞氯化钠注射液(石药集团恩必普药业有限公司,国药准字H20100041,100 mL:丁苯酞25 mg与氯化钠0.9 g)静滴,100 mL/12 h,连续滴注2周。治疗后2组定期随访至治疗后3个月,对比2组治疗效果。
1.3 观察指标 (1)分别于治疗前与治疗后3 d、7 d、1个月及3个月采用NHISS[5]评估神经功能,NHISS评分越低,患者神经功能恢复越良好;治疗后3个月评估神经功能改善情况:NHISS评分降低90%~100%者为痊愈;NHISS评分降低45%~89%者为显效;NHISS评分降低18%~44%者为有效;NHISS评分降低<18%或未降低者为无效;总有效=痊愈+显效+有效。(2)分别于治疗前与治疗后3 d、7 d、1个月及3个月采用MMSE及MoCA量表[6]评估患者认知功能,经校正受教育程度偏倚后进行评分,其中MMSE评分≥25分为认知功能正常,14~24分为认知功能障碍,≤13分为痴呆;MoCA评分≥26分为正常,<26分为认知功能障碍。
1.4 统计学方法 采用SPSS 20.0软件进行数据分析,计量资料以均数±标准差( x±s)表示,组间比较采用t检验,组内多个时间点比较采用单因素方差分析;计数资料以百分比(%)表示,采用χ2检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
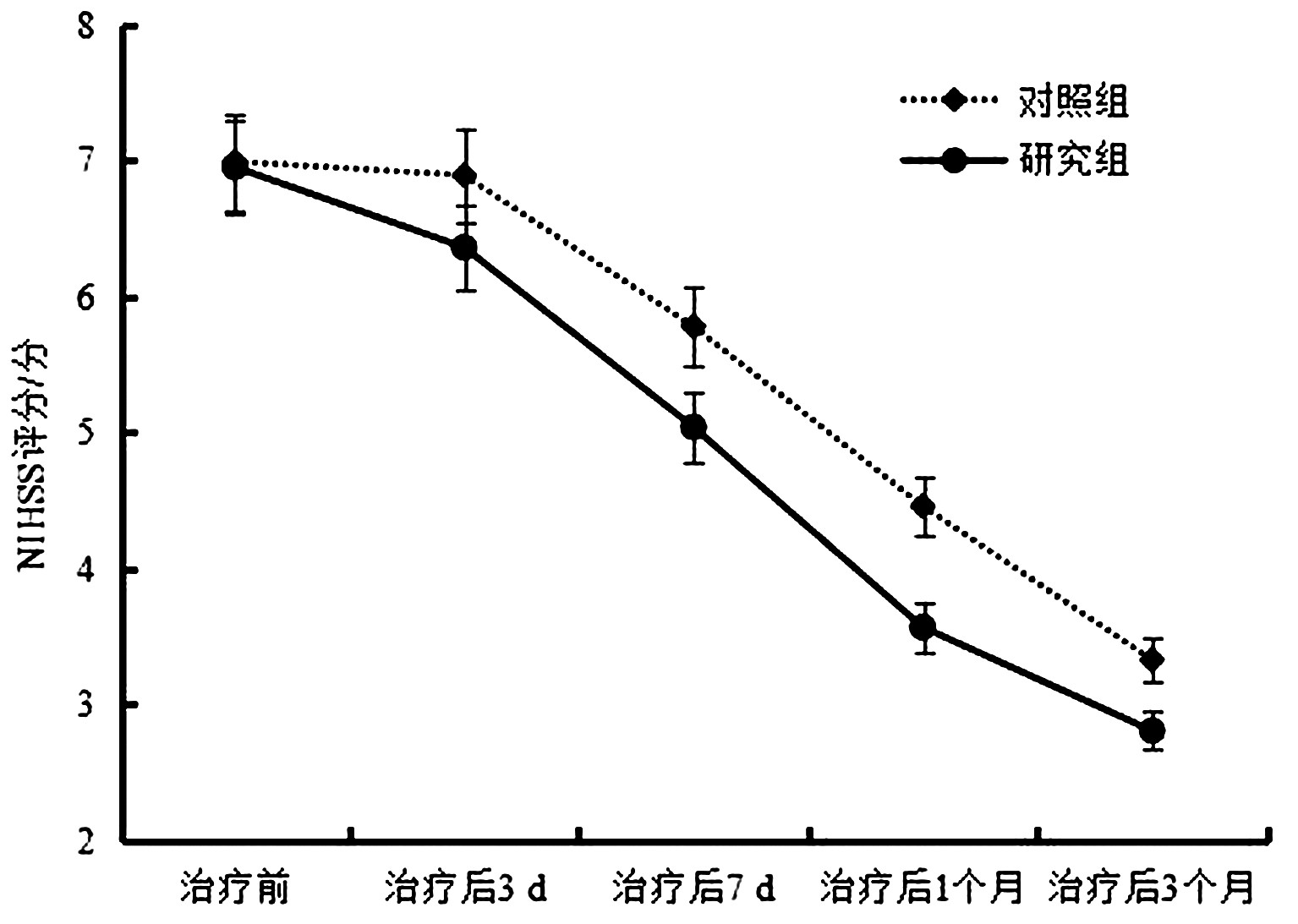
2.1 2组治疗前后NIHSS评分比较 与治疗前比,治疗后3 d~3个月2组NIHSS评分逐渐降低(P<0.01),且治疗后1、3个月研究组NIHSS评分低于对照组(P<0.05)。见表2、图1。
2.2 2组治疗前后神经功能改善情况比较 治疗后3个月研究组神经功能痊愈22例,显效13例,有效11例,无效7例,总有效率86.79%(46/53);对照组神经功能痊愈15例,显效9例,有效12例,无效17例,总有效率67.92%(36/53)。研究组神经功能改善总有效率显著高于对照组(χ2=5.386,P=0.020)。
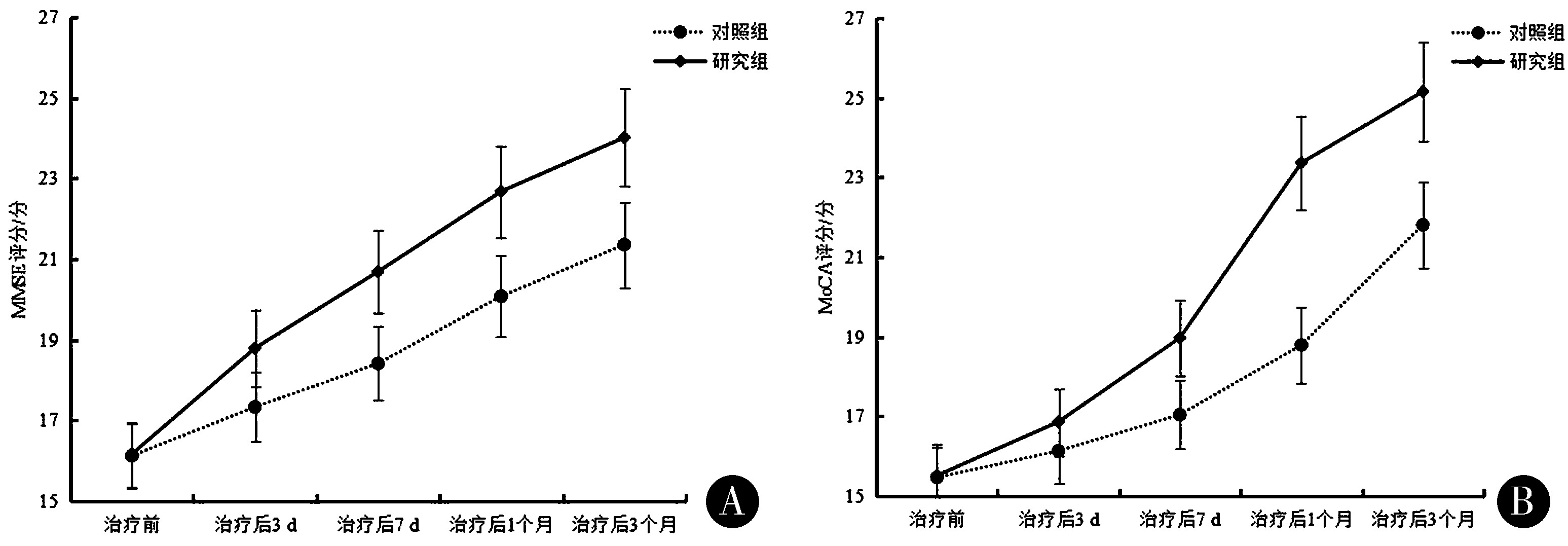
2.3 2组治疗前后MMSE评分及MoCA评分比较 与治疗前比较,治疗后3 d~3个月2组MMSE评分及MoCA评分均呈逐渐升高趋势(P<0.01);且治疗后3 d、7 d、1个月及3个月研究组MMSE评分高于对照组(P<0.05或0.01);治疗后7 d、1个月及3个月研究组MoCA评分均高于对照组(P<0.05或0.01)。见表3、图2。
表1 2组一般资料比较
Table 1 Comparison of general information of 2 groups
| 组别 |
n |
性别(男/女) |
年龄/岁 |
文化程度 |
|
合并疾病 |
| 小学及以下 |
初中 |
高中及中专 |
大专及以上 |
|
高血压 |
高脂血症 |
糖尿病 |
| 对照组 |
53 |
27/26 |
53.41±8.16 |
9 |
25 |
6 |
13 |
|
11 |
10 |
8 |
| 研究组 |
53 |
25/28 |
52.98±8.74 |
7 |
31 |
7 |
8 |
|
9 |
13 |
7 |
| t/χ2值 |
|
0.151 |
0.262 |
1.363 |
|
0.658 |
| P值 |
|
0.698 |
0.794 |
0.506 |
|
0.72 |
表2 2组治疗前后NIHSS评分比较 ( x±s,分)
Table 2 Comparison of NIHSS scores before and after treatment in 2 groups ( x±s,score)
| 组别 |
n |
治疗前 |
治疗后3 d |
治疗后7 d |
治疗后1个月 |
治疗后3个月 |
F值 |
P值 |
| 对照组 |
53 |
6.99±2.12 |
6.89±2.07 |
5.78±1.96 |
4.46±1.87 |
3.33±1.25 |
31.95 |
0.000 |
| 研究组 |
53 |
6.95±2.14 |
6.36±2.03 |
5.04±1.94 |
3.57±1.85 |
2.81±1.23 |
85.887 |
0.000 |
| t值 |
|
0.097 |
1.331 |
1.954 |
2.463 |
2.159 |
|
|
| P值 |
|
0.923 |
0.186 |
0.053 |
0.015 |
0.033 |
|
|
表3 2组治疗前后MMSE评分及MoCA评分比较 ( x±s,分)
Table 3 Comparison of MMSE scores and MoCA scores before and after treatment in 2 groups ( x±s,scoer)
| 指标 |
组别 |
n |
治疗前 |
治疗后3 d |
治疗后7 d |
治疗后1个月 |
治疗后3个月 |
F值 |
P值 |
| MMSE评分 |
对照组 |
53 |
16.12±3.87 |
17.33±3.48 |
18.41±3.32 |
20.08±3.27 |
21.36±3.08 |
26.236 |
0.000 |
| |
研究组 |
53 |
16.16±3.85 |
18.79±3.51 |
20.69±3.27 |
22.68±3.24 |
24.02±3.12 |
57.984 |
0.000 |
| |
t值 |
|
0.053 |
2.15 |
3.562 |
4.112 |
4.417 |
|
|
| |
P值 |
|
0.958 |
0.034 |
0.001 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
|
|
| MoCA评分 |
对照组 |
53 |
15.46±4.02 |
16.13±4.11 |
17.04±3.96 |
18.79±3.49 |
21.81±3.16 |
32.096 |
0.000 |
| |
研究组 |
53 |
15.51±4.06 |
16.86±4.09 |
18.97±3.87 |
23.37±3.53 |
25.16±3.18 |
85.887 |
0.000 |
| |
t值 |
|
0.064 |
0.917 |
2.538 |
6.717 |
5.44 |
|
|
| |
P值 |
|
0.949 |
0.361 |
0.013 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
|
|
图1 2 组治疗前后神经功能评分比较
Figure 1 Comparison of neurological function score before and after treatment in 2 groups
图2 2组治疗前后认知功能比较
Figure 2 Comparison of cognitive function before and after treatment in 2 groups
2.4 安全性分析 2组治疗期间均未出现严重不良反应,偶尔可见轻微呕吐、恶心症状,停药后均可自行缓解。
3 讨论
急性脑卒中已成为目前成人致残的关键因素,其中急性缺血性脑卒中占比达70%以上[23-29]。研究[30-36]报道,急性缺血性脑卒中患者由轻度认知功能障碍发展至痴呆的风险增大,导致神经功能及认知缺陷加重,因此积极有效的脑神经保护治疗对于缓解急性缺血性脑卒中患者神经功能缺损,改善认知及预后至关重要[37-42]。但目前临床治疗主要集中于抗血栓治疗,尚缺乏有效的神经保护及脑保护治疗,因此整体疗效并不理想。
丁苯酞是中国自主研制的一种新型神经保护药物,具有较好的神经保护作用,已经广泛用于心脑血管疾病的治疗[43]。急性缺血性脑卒中患者早期表现为记忆力、计算力、判断力、语言能力及抽象思维能力降低,认知功能及神经功能缺陷,随着疾病进展,可逐渐发展为痴呆综合征。研究[44]报道,丁苯酞注射液可调节脑组织线粒体功能,升高脑血管内皮一氧化氮及前列腺素水平,改善血管内皮细胞功能;还可抗血小板聚集,减少谷氨酸释放,降低血栓素A2合成及细胞内钙浓度,抑制动脉粥样硬化的炎症反应,增加缺血区局部脑组织血流量,恢复脑缺血缺氧状态下脑组织能量代谢,抑制脑神经细胞凋亡,促进患者神经功能恢复。本研究显示,研究组神经功能改善总有效率显著高于对照组,且治疗后3 d~3个月2组NIHSS评分逐渐降低,治疗后1、3个月研究组NIHSS评分低于对照组,提示丁苯酞注射液可改善急性缺血性脑卒中患者神经损害。
自由基具可破坏细胞膜的通透性、流动性及完整性,致细胞膜及溶酶体损伤,造成局部脑组织损伤,损害学习记忆能力,造成认知障碍,在心脑血管病发生及进展中具有重要作用[45-46]。研究[47-48]报道,丁苯酞除具有多靶点抗血栓、抗脑缺血及抗血小板聚集等作用外,还可有效清除自由基,缓解大脑缺血缺氧损伤,已经广泛用于缺血性脑血管病、痴呆等神经系统疾病中。本研究中,治疗后3 d~3个月2组MMSE评分及MoCA评分逐渐升高,且治疗后3 d、7 d、1个月及3个月研究组MMSE评分高于对照组;治疗后7 d、1个月及3个月研究组MoCA评分高于对照组,与研究[17]结果相似,证实丁苯酞注射液可改善急性缺血性脑卒中患者认知。此外,2组治疗期间均未见明显不良反应,提示丁苯酞注射液对急性缺血性脑卒中患者具有良好的安全性。
4 参考文献
[1] JAUCH E C,SAVER J L,ADAMS H P,et al.Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association[J].Stroke,2013,44(3):870-947.
[2] CUMMING T B,BLOMSTRAND C,BERNHARDT J,et al.The NIH stroke scale can establish cognitive function after stroke[J].Cerebrovasc Dis,2010,30(1):7-14.
[3] BERKHEMER O A,FRANSEN P S,BEUMER D,et al.A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke[J].J Emerg Med,2015,48(4):11-11.
[4] SUN M S,JIN H,SUN X,et al.Free Radical Damage in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury:An Obstacle in Acute Ischemic Stroke after Revascularization Therapy[J].Oxid Med Cell Longev,2018:3804979.doi:10.1155/2018/3804979.
[5] 段淑娟.丁苯酞注射液对缺血性脑卒中患者认知功能及脑血流灌注的影响[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2017,20(6):104-107.
[6] CHEN N,ZHOU Z,LI J,et al.3-n-butylphthalide exerts neuroprotective effects by enhancing anti-oxidation andattenuating mitochondrial dysfunction in an in vitro model of ischemic stroke[J].Drug Des Devel Ther,2018,12:4 261-4 271.doi:10.2147/DDDT.S189472.
[7] WANG L,WANG X,LI T,et al.8e Protects against Acute Cerebral Ischemia by Inhibition of PI3Kγ-Mediated Superoxide Generation in Microglia[J].Molecules,2018,23(11).doi:10.3390/molecules23112828.
[8] ZENG G R,ZHOU S D,SHAO Y J,et al.Effect of Ginkgo biloba extract-761 on motor functions in permanentmiddle cerebral artery occlusion rats[J].Phytomedicine,2018,48:94-103.doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2018.05.003.
[9] LI F,MA Q,ZHAO H,et al.L-3-n-Butylphthalide reduces ischemic stroke injury and increases M2 microglialpolarization[J].Metab Brain Dis,2018,33(6):1 995-2 003.doi:10.1007/s11011-018-0307-2.
[10] HUANG L,WANG S,MA F,et al.Fromstroke to neurodegenerative diseases:The multi-target neuroprote-ctive effects of3-n-butylphthalide and its derivatives[J].Pharmacol Res,2018,135:201-211.doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2018.08.007.
[11] WANG S,MA F,HUANG L,et al.Dl-3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP):A Promising Therapeutic Agent for Ischemic Stroke[J].CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets,2018,17(5):338-347.doi:10.2174/1871527317666180612125843.
[12] QIN C,ZHOU P,WANG L,et al.Dl-3-N-butylphthalide attenuates ischemic reperfusion injury by improving thefunction of cerebral artery and circulation[J].J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2018 May15:271678X18776833.doi:10.1177/0271678X18776833.
[13] LIN Z,RAO X,ZHANG Z,et al.Economic evaluation of human urinarykallindinogenase for patients with acute ischemic stroke in China[J].J Med Econ,2018,21(8):778-783.doi:10.1080/13696998.2018.1470977.
[14] ZHANG P,XU R,GUO Y,et al.DL-3-n-butylphthalidepromotes dendrite development in cortical neurons subjected to oxygen-glucosedeprivation/reperfusion[J].Cell Biol Int,2018,42(8):1 041-1 049.doi:10.1002/cbin.10980.
[15] QIU H,MA J,WU H,et al.DL-3-n-butylphthalide improves ventricular function,and prevents ventricular remodeling and arrhythmias in post-MI rats[J].Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol,2018,391(6):627-637.doi:10.1007/s00210-018-1490-8.
[16] YAN R Y,WANG S J,YAO G T,et al.The protective effect and its mechanism of 3-n-butylphthalide pretreatment on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in rats[J].Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2017,21(22):5 275-5 282.doi:10.26355/eurrev_201711_13852.
[17] WANG Y,QI W,ZHANG L,et al.The novel targets of DL-3-n-butylphthalide predicted bysimilarity ensemble approach in combination with molecular docking study[J].QuantImaging Med Surg,2017,7(5):532-536.doi:10.21037/qims.2017.10.08.
[18] LIU R Z,FAN C X,ZHANG Z L,et al.Effects ofDl-3-n-butylphthalide on Cerebral Ischemia Infarction in Rat Model by MassSpectrometry Imaging[J].Int J Mol Sci,2017,18(11).doi:10.3390/ijms18112451.
[19] TIAN Z,WANG J,WANG Y,et al.Effects of butylphthalide oncognitive decline in diabetic rats[J].Mol Med Rep,2017,16(6):9 131-9 136.doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.7700.
[20] LI J,XU S F,PENG Y,et al.Conversion and pharmacokineticsprofiles of a novel pro-drug of 3-n-butylphthalide,potassium2-(1-hydroxypentyl)-benzoate,in rats and dogs[J].Acta Pharmacol Sin,2018,39(2):275-285.doi:10.1038/aps.2017.90.
[21] FENG L,SHARMA A,NIU F,et al.TiO(2)-Nanowired Delivery of DL-3-n-butylphthalide (DL-NBP)Attenuates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption,Brain Edema Formation,and NeuronalDamages Following Concussive Head Injury[J].Mol Neurobiol,2018,55(1):350-358.doi:10.1007/s12035-017-0746-5.
[22] XIONG Z,LU W,ZHU L,et al.Dl-3-n-Butylphthalide Treatment Enhances Hemodynamics and AmelioratesMemory Deficits in Rats with Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion[J].Front AgingNeurosci,2017,9:238.doi:10.3389/fnagi.2017.00238.
[23] ZHANG C,ZHAO S,ZANG Y,et al.The efficacy andsafety of Dl-3n-butylphthalide on progressive cerebral infarction:A randomizedcontrolled STROBE study[J].Medicine,2017,96(30):e7257.doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000007257.
[24] TIAN X,HE W,YANG R,et al.Dl-3-n-butylphthalide protects the heart against ischemic injury and H9c2 cardiomyoblasts against oxidative stress:involvement of mitochondrial function and biogenesis[J].J Biomed Sci,2017,24(1):38.doi:10.1186/s12929-017-0345-9.
[25] SUN Y,CHENG X,WANG H,et al.dl-3-n-butylphthalide promotes neuroplasticity and motor recovery in stroke rats[J].Behav Brain Res,2017,329:67-74.doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2017.04.039.
[26] LI J,WANG X L,WANG A P,et al.Toxicokinetics and toxicity ofpotassium 2-(1-hydroxypentyl)-benzoate in beagle dogs[J].J Asian Nat Prod Res,2017,19(4):388-401.doi:10.1080/10286020.2017.1302940.
[27] WANG X L,WANG Z Y,LING J J,et al.Synthesis and biologicalevaluation of nitric oxide (NO)-hydrogen sulfide (H(2)S) releasing derivatives of(S)-3-n-butylphthalide as potential antiplatelet agents[J].Chin J Nat Med,2016,14(12):946-953.doi:10.1016/S1875-5364(17)30021-3.
[28] YAN H,YAN Z,NIU X,et al.Dl-3-n-butylphthalide canimprove the cognitive function of patients with acute ischemic stroke:aprospective intervention study[J].Neurol Res,2017,39(4):337-343.doi:10.1080/01616412.2016.1268775.
[29] ABDOULAYE I A,GUO Y J.A Review of Recent Advances in NeuroprotectivePotential of 3-N-Butylphtha-lide and Its Derivatives[J].Biomed Res Int,2016:5012341.doi:10.1155/2016/5012341.
[30] CHEN X,WANG K.The fate of medications evaluated for ischemic strokepharmacotherapy over the period 1995-2015[J].Acta Pharm Sin B,2016,6(6):522-530.
[31] ZHOU J,ZHANG Y H,SONG H Z,et al.5d,a novel analogue of 3-n-butylphthalide,decreases NADPH oxidase activitythrough the positive regulation of CK2 after ischemia/reperfusion injury[J].Oncotarget,2016,7(26):39 444-39 457.doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8548.
[32] ZHANG P,GUO Z F,XU Y M,et al.N-Butylphthalide (NBP) amelioratedcerebral ischemia reperfusion-induced brain injury via HGF-regulated TLR4/NF-κBsignaling pathway[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2016,83:658-666.doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.07.040.
[33] ZHANG L,PUCHOWICZ M A,LAMANNA J C,et al.Protective Effect ofDl-3-n-Butylphthalide on Recovery from Cardiac Arrest and Resuscitation in Rats[J].Adv Exp Med Biol,2016,923:31-36.doi:10.1007/978-3-319-38810-6_4.
[34] XUE L X,ZHANG T,ZHAO Y W,et al.Efficacy and safetycomparison of DL-3-n-butylphthalide and Cerebrolysin:Effects on neurological andbehavioral outcomes in acute ischemic stroke[J].Exp Ther Med,2016,11(5):2 015-2 020.
[35] TIAN X,LIU B,ZHANG Y,et al.LC-MS/MSAnalysis and Pharmacokinetics of Sodium (±)-5-Bromo-2-(α-hydroxypentyl) Benzoate(BZP),an Innovative Potent Anti-Ischemic Stroke Agent in Rats[J].Molecules,2016,21(4):501.doi:10.3390/molecules21040501.
[36] YIN W,LAN L,HUANG Z,et al.Discovery of a ring-opened derivative of 3-n-butylphthalide bearingNO/H2S-donating moieties as a potential anti-ischemic stroke agent[J].Eur J MedChem,2016,115:369-380.doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.03.044.
[37] CHEN M,LIU Q,TAN M,et al.Synthesis and biological evaluationof n-butylphthalide derivatives as anti-platelet aggregation agents[J].Nat ProdRes,2016 Feb 15:1-4.
[38] ZHAO H,YUN W,ZHANG Q,et al.Mobilization ofCirculating Endothelial Progenitor Cells by dl-3-n-Butylphthalide in AcuteIschemic Stroke Patients[J].J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis,2016,25(4):752-760.doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2015.11.018.
[39] JIANG Y,SUN L,XUAN X,et al.Impacts of N-Butylphthalide on expression of growth factors in rats with focal cerebral ischemia[J].Bosn J Basic Med Sci,2016,16(2):102-107.doi:10.17305/bjbms.2016.560.
[40] WANG F,MA J,HAN F,et al.DL-3-n-butylphthalide delays the onset and progression of diabetic cataract byinhibiting oxidative stress in rat diabetic model[J].Sci Rep,2016,6:19396.doi:10.1038/srep19396.
[41] ZHOU Y,NIU LJ,QI FM,et al.Effect of 3-n-butylphthalide pretreatment on expression of the HSP70 after brain ischemia/reperfusion[J].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi,2015,31(2):136-140.
[42] YANG LC,LI J,XU SF,et al.L-3-n-butylphthalide Promotes Neurogenesis and Neuroplasticityin Cerebral Ischemic Rats[J].CNS Neurosci Ther,2015,21(9):733-741.doi:10.1111/cns.12438.
[43] SHENG X,HUA K,YANG C,et al.Novel hybridsof 3-n-butylphthalide and edaravone:Design,synthesis and evaluations aspotential anti-ischemic stroke agents[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2015,25(17):3 535-3 540.doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.06.090.
[44] LAN Z,XU X,XU W,et al.Discovery of3-n-butyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindol-1-one as a potential anti-ischemic strokeagent[J].Drug Des Devel Ther,2015,9:3 377-3 391.doi:10.2147/DDDT.S84731.
[45] HUA K,SHENG X,LI TT,et al.The edaravone and3-n-butylphthalide ring-opening derivative 10b effectively attenuates cerebralischemia injury in rats[J].Acta Pharmacol Sin,2015,36(8):917-927.doi:10.1038/aps.2015.31.
[46] ZHAO W,LUO C,WANG J,et al.3-N-butylphthalide improves neuronal morphology after chronic cerebral ischemia[J].Neural Regen Res,2014,9(7):719-726.doi:10.4103/1673-5374.131576.
[47] WANG X,WANG L,SHENG X,et al.Design,synthesis and biological evaluation of hydrogen sulfide releasingderivatives of 3-n-butylphthalide as potential antiplatelet and antithromboticagents[J].Org Biomol Chem,2014,12(31):5 995-6 004.doi:10.1039/c4ob00830h.
[48] ZHANG T,WANG H,LI Q,et al.Modulating autophagy affectsneuroamyloidogenesis in an in vitro ischemic stroke model[J].Neuroscience,2014,263:130-137.doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.01.012.
(收稿2018-06-25 修回2018-10-12)
本文责编:夏保军
本文引用信息:赵琰,李华,王景涛.丁苯酞注射液对急性缺血性脑卒中患者神经功能及认知的影响[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2018,21(24):2708-2713.DOI:10.12083/SYSJ.2018.24.565
Reference information:ZHAO Yan,LI Hua,WANG Jingtao.Effect of butylphthalide injection on the nerve function and cognition of acute ischemic stroke patients[J].Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases,2018,21(24):2708-2713.DOI:10.12083/SYSJ.2018.24.565