目的 评价血管内治疗破裂前交通动脉瘤的有效性及患者的总体预后。方法 收集2014-03-2018-06行血管内介入治疗的60例破裂前交通动脉瘤患者的病例资料,分析动脉瘤栓塞率、术前术后GCS评分(Glasgow Coma Scale,GCS)、支架的使用、动脉瘤复发、并发症及GOS评分(Glasgow Outcome Scale,GOS)判断预后等。结果 动脉瘤填塞Raymond分级:Ⅰ级50例,Ⅱ级6例,Ⅲ级4例;19例术中使用支架(支架组和非支架组在早期动脉瘤栓塞率差异无统计学意义,P=0.88
血管内介入治疗破裂前交通动脉瘤的疗效分析
程 哲 闵敬亮 杨 光 张 辉 王 昊 束汉生△
蚌埠医学院第二附属医院,安徽 蚌埠 233000
作者简介:程哲,Email:794585335@qq.com
△通信作者:来汉生,Email:shuhansheng@163.com
【摘要】 目的 评价血管内治疗破裂前交通动脉瘤的有效性及患者的总体预后。方法 收集2014-03-2018-06行血管内介入治疗的60例破裂前交通动脉瘤患者的病例资料,分析动脉瘤栓塞率、术前术后GCS评分(Glasgow Coma Scale,GCS)、支架的使用、动脉瘤复发、并发症及GOS评分(Glasgow Outcome Scale,GOS)判断预后等。结果 动脉瘤填塞Raymond分级:Ⅰ级50例,Ⅱ级6例,Ⅲ级4例;19例术中使用支架(支架组和非支架组在早期动脉瘤栓塞率差异无统计学意义,P=0.883);40例患者在术后1 a内行DSA随访,8例出现动脉瘤复发(支架组与非支架组复发率差异无统计学意义,P=0.689);术后GCS评分较术前明显改善(Z=-3.741,P<0.01);末次随访患者GOS评分:5分43例,4分10例,3分4例,2分2例,1分1例;术后出现脑积水6例,脑梗死7例,肺部感染4例。结论 个体化的血管内介入治疗破裂前交通动脉瘤安全有效并显著改善患者临床症状与预后。
【关键词】 前交通动脉瘤;破裂动脉瘤;血管内介入治疗;并发症;预后
【中图分类号】 R739.4 【文献标识码】 A 【文章编号】 1673-5110(2018)21-2331-07 DOI:10.12083/SYSJ.2018.21.501
Efficacy analysis of endovascular interventional treatment for ruptured anterior communicating artery aneurysms
CHENG Zhe,MIN Jingliang,YANG Guang,ZHANG Hui,WANG Hao,SHU Hansheng
The Second Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College,Bengbu 233000,China
【Abstract】 Objective To evaluate the effectiveness of endovascular treatment of ruptured anterior communicating aneurysms (AcoA) and the overall prognosis of patients.Methods The data of 60 patients with ruptured AcoA who underwent endovascular intervention from March 2014 to June 2018 were collected.The aneurysm embolization rate,preoperative and postoperative GCS score,stent use,aneurysm recurrence,complications,and GOS score to determine prognosis.Results Raymond classification of aneurysm:50 cases of grade I,6 cases of grade II,4 cases of grade III;19 cases of stents used during the operation (the stenting group and the non-stent group had no statistical difference in early aneurysm embolization rate,P=0.883);Forty patients underwent DSA follow-up within 1 year after operation,and 8 patients had aneurysm recurrence (no difference in the recurrence rate between the stent group and the non-stent group,P=0.689).The postoperative GCS score was significantly improved compared with the preoperative (Z=-3.741,P<0.01);GOS score at the last follow-up:5 points in 43 cases;4 points in 10 cases;3 points in 4 cases;2 points in 2 cases;1 point in 1 case;postoperative hydrocephalus occurred in 6 cases,cerebral infarction In 7 cases,4 cases of pulmonary infection.Conclusion Individualized endovascular intervention for the treatment of ruptured anterior communicating aneurysms is safe and effective and significantly improves the patient's clinical symptoms and prognosis.
【Key words】 Anterior communicating aneurysm;Ruptured aneurysm;Endovascular intervention;Complications;Prognosis
前交通动脉瘤占颅内破裂动脉瘤的25%~39%[1-5]。前交通动脉复合体在解剖上复杂、穿支血管丰富且变异较多[6-7],前交通动脉瘤破裂率高[8-9],同时破裂后容易形成纵裂或额叶血肿,加上急性期脑水肿严重导致颅内压力极高,选择开颅夹闭前交通动脉瘤难度大且创伤重。随神经介入技术及材料的发展,血管内治疗破裂前交通动脉瘤逐步成为最佳治疗方案[10-14]。本文回顾分析2014-03-2018-06于蚌埠医学院第二附属医院神经外科行血管内治疗的60例破裂前交通动脉瘤患者的临床资料,以评价血管内治疗破裂前交通动脉瘤的有效性及患者的总体预后。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料 男27例,女33例;年龄:37~85岁,平均57.53岁;入院时Hunt-Hess分级Ⅰ~Ⅱ级30例,Ⅲ级22例,Ⅳ~Ⅴ级8例;术前GCS(Glasgow Coma Scale)评分:15~13分34例;12~10分13例;≤9分13例;行头颅CT检查均表现为蛛网膜下腔出血(其中合并前纵裂血肿、脑室内积血或额叶血肿10例);进一步CTA或DSA检查示,60例均为前交通动脉瘤破裂;动脉瘤<5 mm 29例,5~15 mm 23例,>15 mm 8例。基础疾病:高血压20例,糖尿病10例,糖尿病合并高血压8例。
1.2 手术方法 采用气管插管全身麻醉,全身肝素化,Seldinger技术在股动脉置入6F动脉鞘,选用5F造影导管行双侧颈内颈外及椎动脉造影,行3D三维重建,选择最佳工作角度,将塑形微导管超选进入动脉瘤腔内,根据动脉瘤大小选用不同可解脱弹簧圈(来自Stryker公司、MicroVention公司),术中根据动脉瘤颈及A1和A2角度等选择性使用支架(Neuroform EZ、Enterprise、LVIS、Solitaire AB支架)。每次释放支架或解脱弹簧圈时,均行血管造影,确定弹簧圈在动脉瘤内,观察载瘤动脉及其分支通畅情况以及填塞致密程度。术前、术后抗凝(根据是否支架辅助)及抗血小板治疗,术前CTA或DSA评估可能需要使用支架时,择期手术时术前3 d应经胃肠道联合抗血小板(阿司匹林肠溶片100 mg/d,硫酸氢氯吡格雷片75 mg/d),急诊手术时术前6 h应(阿司匹林肠溶片300 mg,硫酸氢氯吡格雷片225 mg)。当颅内释放支架后或考虑急诊血栓形成,常规替罗非班静脉内泵入维持。
1.3 随访 随访期间40例在介入术后半年至1 a内行DSA造影复查;电话结合门诊询问患者,记录术后第6个月的GOS评分及GCS评分。
1.4 统计学方法 采用SPSS 18.0软件处理数据,采取卡方检验、Fisher's确切概率检验或秩和检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 影像学结果 术前常规DSA造影发现颅内多发动脉瘤7例,其中前交通动脉瘤均为责任动脉瘤;动脉瘤栓塞过程中出现3例术中破裂;术中动脉瘤栓塞按照Raymond分级:Ⅰ级(瘤颈瘤腔造影剂均不显影)完全栓塞50例(83.3%),Ⅱ级(瘤体不显影瘤颈部分显影)次全栓塞6例(10%),Ⅲ级(瘤腔造影剂滞留)不全栓塞4例(6.7%)。其中支架组和非支架组在早期动脉瘤栓塞率上差异无统计学意义(Z=-0.147,P=0.883)。见表1。
2.2 支架使用情况 19例动脉瘤术中植入支架,其中Neuroform支架6个,Enterprise支架5个,LVIS支架2个,Solitaire AB支架6个;4例为相对宽颈(动脉瘤颈体比大于1/2),5例绝对宽颈动脉瘤(动脉瘤颈≥4 mm);19例支架植入患者中均表现为单侧A1缺如或重度发育不良;19例支架使用患者中出现手术相关并发症5例,41例非支架使用患者中出现并发症者为12例(χ2=0.056,P=0.813),支架组与非支架组手术相关并发症比较差异无统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表1。
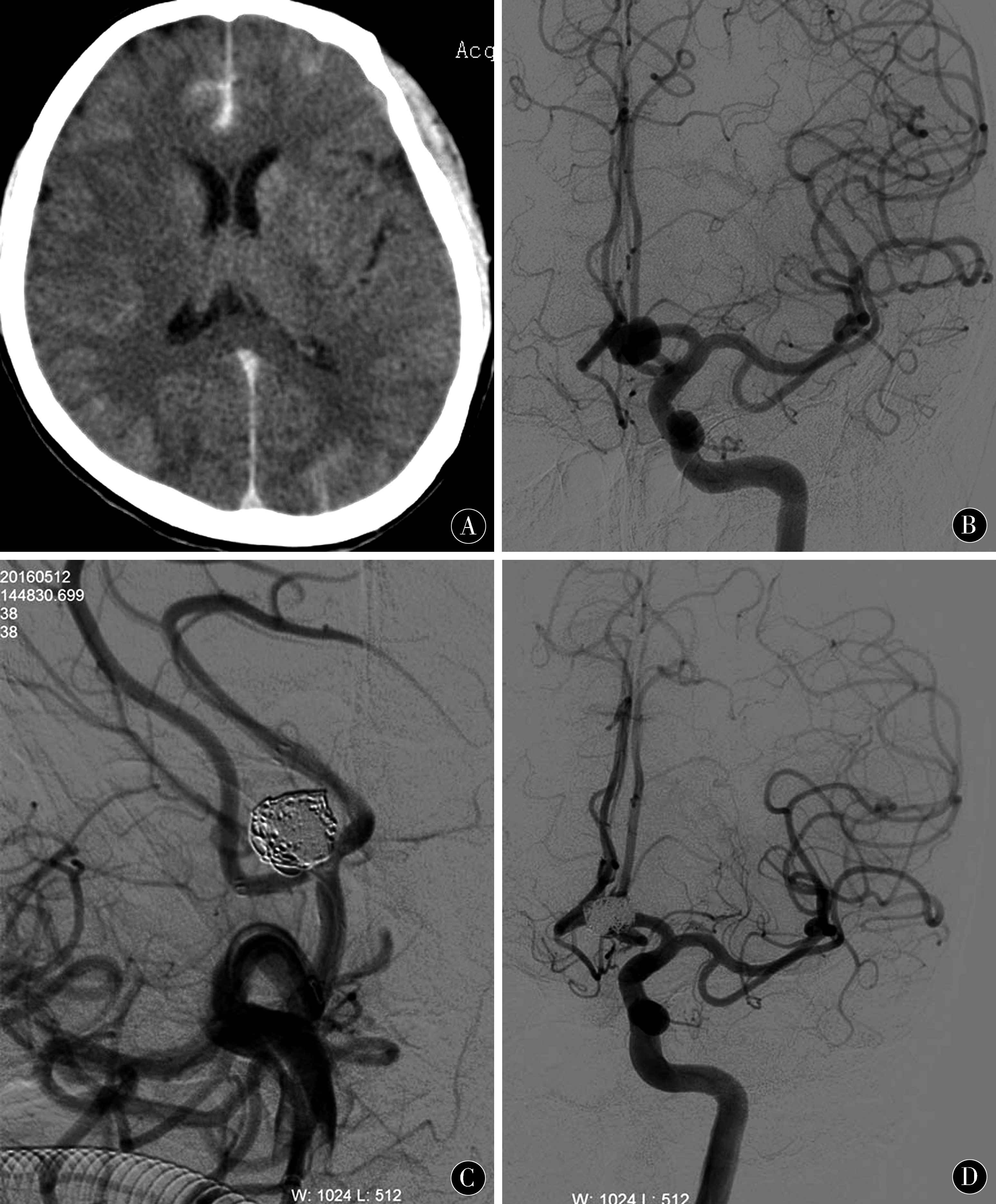
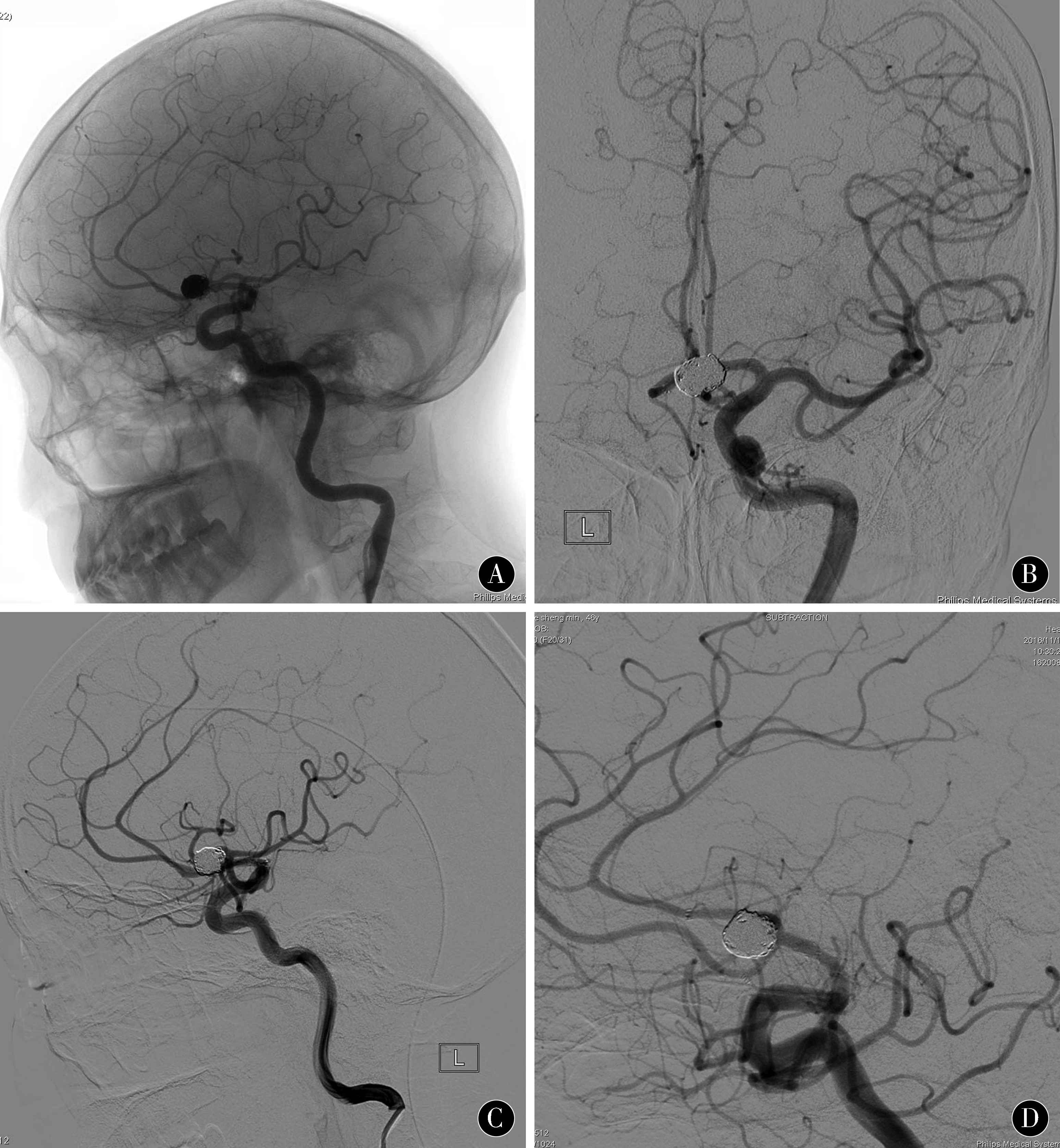
2.3 典型病例 患者 女,59岁,突发剧烈头痛6 h入院,头颅CT检查发现前纵裂池蛛网膜下腔出血(图1A),急诊行DSA造影发现前交通动脉瘤,瘤体呈类球形,约11.1 mm×9.7 mm大小,瘤颈7.5 mm(图1B、C),右侧大脑前动脉A1段缺如,双侧大脑前动脉A2段自瘤体底部发出,术中Y型支架辅助栓塞,术后造影显示双侧A2血流通畅,瘤腔填塞满意(图1D);半年后复查DSA未见动脉瘤复发,瘤颈未见异常,弹簧圈及支架在位(图2)。
表1 支架辅助栓塞与单纯栓塞破裂前交通动脉瘤的栓塞率、复发率、并发症与预后比较
Table 1 Comparison of embolization rate,recurrence rate,complications and prognosis between stent-assisted
embolization and simple embolization for ruptured anterior communicating artery aneurysms
| 组别 |
n |
Raymond分级 |
复发 |
并发症 |
| Ⅰ级 |
Ⅱ级 |
Ⅲ级 |
| 支架组 |
19 |
16 |
2 |
1 |
2/14 |
5 |
| 非支架组 |
41 |
34 |
4 |
3 |
6/26 |
12 |
| Z/χ2值 |
|
Z=-0.147 |
|
χ2=0.056 |
| P值 |
|
0.883 |
|
0.813 |
注:经秩和检验,支架组和非支架组在早期动脉瘤栓塞率上未见显著差异;经Fisher's 检测,支架组与非支架组复发未见显著差异;经Pearson Chi-square检验,支架组与非支架组出现相关并发症未见显著差异
图1 支架辅助栓塞破裂前交通动脉瘤:患者女性,59岁,突发剧烈头痛6 h。A:头颅CT提示前纵裂池蛛网膜下腔出血;B~D:前交通动脉瘤,瘤体呈类球形,顶端有瘤疱,大小约11.1 mm×9.7 mm大小,瘤颈7.5 mm,右侧A1段缺如,双侧A2段自瘤体底部发出,术中顺利植入Y形双支架,术后造影显示瘤腔填塞满意,血管通畅
Figure 1 Stent assisted embolization of ruptured anterior communicating artery aneurysm:A female,59 years old,presented with severe headache for 6 h.A:Anterior longitudinal fissure cistern subarachnoid hemorrhage was found in head CT;B~D:Anterior communicating artery aneurysm were spherical in shape,about 11.1 mm *9.7 mm in size,7.5 mm in neck,absence of right A1 segment,bilateral A2 segment from the base of the aneurysm,Y-shaped double stents were successfully implanted during the operation,Postoperative angiography showed that the aneurysm was filled satisfactorily and the vessels were unobstructed
2.4 造影随访 介入术后半年至1 a内40例(14例使用支架,26例未使用支架)复查DSA造影检查,其中支架组中复发2例,非支架组中复发6例。经Fisher's 检测,支架组与非支架组复发差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表1。
2.5 临床结果 术后6例出现脑积水症状,7例出现脑梗死,4例出现肺部感染;随访末期患者GOS评分:5分43例;4分10例;3分4例;2分2例;1分1例(见表1);对60患者末期随访时再次进行GCS评分,与术前相比差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。见表2。
图2 支架辅助栓塞破裂前交通动脉瘤 A~D:患者术后6个月复查造影未见动脉瘤复发
Figure 2 Stent assisted embolization of ruptured anterior communicating artery aneurysm A-D:No recurrence was found at 6 months after operation
表2 破裂前交通动脉瘤术前和末次随访GCS评分比较
Table 2 Comparison of pre-operative and last follow-up GCS scores in patients with
ruptured anterior communicating artery aneurysms
| 手术前后 |
GCS评分 |
GCS评分(M±St) |
Z值 |
P值 |
| 15~13 |
12~10 |
≤9 |
| 术前 |
34 |
13 |
13 |
11.933±2.990 |
-3.741 |
<0.01 |
| 末次随访 |
54 |
2 |
4 |
13.850±1.783 |
|
|
3 讨论
前交通动脉瘤的形成与局部血管解剖变异、血管结构扭曲及血流动力学影响密切相关[15-17]。引起前交通动脉瘤破裂的原因是多因素的[18-19]。开颅夹闭前交通动脉瘤常因额叶的牵拉及直回切除引起脑副损伤较多,术后并发症多、创伤较大。优先选择血管内介入治疗破裂前交通动脉瘤[20-21],患者有着更低的致残率及致死率[22-23]。颅内动脉瘤血管内介入治疗专家共识首选推荐介入方案治疗破裂前交通动脉瘤,对于破裂合并颅内血肿或病情较重患者建议行开颅夹闭,开颅夹闭因术中打开蛛网膜间隙释放血性脑脊液有效缓解脑血管痉挛[24]。也要观点认为,血管内栓塞破裂前交通动脉瘤后,再次开颅清除颅内血肿或去骨瓣减压可明显降低手术难度,能有效降低颅内压力、缓解血管痉挛,改善患者总体预后。
既往观点认为,破裂动脉瘤急性期使用颅内支架会显著增加围手术期风险。2012年美国ASA/AHA蛛网膜下腔出血治疗指南评价破裂动脉瘤急性期使用支架仅为Ⅲ类推荐、C级证据[24]。刘建民团队对大量临床资料的追踪研究发现,使用支架辅助治疗急性期破裂动脉瘤相对于单纯填塞,未显著增加围手术期相关并发症发生率和临床随访不良预后率,反而远期疗效更好[25];支架辅助栓塞前交通动脉瘤是安全有效的[26-30]。前交通动脉瘤患者常存在大脑前动脉A1段缺如或重度发育不良,术中为保证前交通及双侧A2段通畅,可选择合适支架辅助栓塞前交通动脉瘤[31-32]。使用支架不仅可以提高宽颈前交通动脉瘤的栓塞率,且可改变载瘤血管的血流动力学,减少动脉瘤的复发率[33]。本次研究报道的19例支架植入患者均为宽颈动脉瘤且均一侧A1缺如或发育不良,与41例非支架患者相比,早期动脉瘤栓塞率差异无统计学意义,与文献[19]报道相符。文献报道,支架辅助栓塞破裂动脉瘤并发症发生率高于非破裂动脉瘤,动脉瘤的不全栓塞及抗血小板治疗均增加了出血风险[34]。本次研究19例支架使用患者中出现手术相关并发症5例,41例非支架使用患者中出现并发症者12例,2组差别无统计学意义,可能是局限于手术例数较少,但与同行结论趋势相符。总之,要谨慎使用支架,做到充分抗凝抗血小板、选择合适病例、不断提高手术技术和尝试新型介入材料。
动脉瘤介入术后有复发的可能性。本组前交通动脉瘤随访病例中支架辅助栓塞复发率为14.3%,单纯栓塞复发率23.0%,与文献报道的单纯栓塞13.2%复发率、支架辅助栓塞5.3%复发率相符[35]。部分复发患者在第1次手术时虽已经做到Raymond分级Ⅰ级栓塞,可能因未使用支架,未能改变大脑前动脉A2段与前交通的夹角,动脉瘤颈因受到血流冲击引起动脉瘤复发[36]。对于术前不完全栓塞或瘤颈有残留的患者,随访复查造影尤为重要,虽然第1次手术达到致密栓塞,然而未改变局部血流动力学,很容易再次复发。
本组患者术前GCS评分(11.933±2.990)分,术后末次随访GCS评分(13.850±1.783)分,前后比较差异有统计学意义,可认为介入手术可以明显改善患者昏迷情况及临床症状。随访末期GOS评分:5分43例,4分10例,3分4例,2分2例,1分1例,绝大多数病人获得较好预后,能够正常独立生活。然而术后相关并发症多集中于高龄、高Hunt-Hess评分及动脉瘤破裂合并脑血肿、脑室出血者。破裂前交通动脉瘤的治疗需要充分结合患者的特点综合选择治疗方案[37-38]。单纯介入栓塞破裂动脉瘤只是该病治疗的第一步,更需要加强呼吸道的管理、预防脑血管事件、快速康复训练等综合治疗[39]。
充分考虑病人术前Hunt-Hess评分、动脉瘤大小及是否宽颈、选择个体化的血管内治疗破裂前交通动脉瘤安全有效且能显著改善患者临床症状,术中支架辅助栓塞安全可靠,能够改善近期预后,使患者获益。
4 参考文献
[1] ZHANG X J,GAO B L,HAO W L,et al.Presence of Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm Is Associated With Age,Bifurcation Angle,and Vessel Diameter[J].Stroke,2018,49(2):341-347.
[2] RIINA H A,LEMOLE GM J R,SPETZLER R F.Anterior communicating ar-tery aneurysms[J].Neurosurg-ery,2002,51:993-996.
[3] UJIIE H,LIEPSCH D W,GOETZ M,et al.Hemo-dynamic study of the anterior communicating artery[J].Stroke,1996,27:2 086-2 093.
[4] BIJLENGA P,EBELING C,JAEGERSBERG M,et al.Risk of rupture of small anterior communicating artery aneurysms is similar to posterior circulation aneurysms[J].Stroke,2013,44(11):3 018-3 026.
[5] BRISMAN J L,SONG J K,NEWELL D W.Cerebral aneurysms[J].N Engl J Med,2006,355:928-939.
[6] ITO H,ONODERA H,WAKUI D,et al.Impact of Aneurysmal Neck Position in Endovascular Therapy for Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms[J].Neurologia MedChir,2016,56(1):21-26.
[7] SHUKLA D P,BHAT D I,DEVI B I.Anterior communicating artery aneurysm presenting with vision loss[J].J Neurosci Rural Pract,2013,4:305-307.
[8] MATSUKAWA H,UEMURA A,FUJII M,et al.Morphological and clinical risk factors for the rupture of anterior communicating artery aneurysms[J].J Neurosu-rg,2013,118(5):978-983.
[9] SHAO X,WANG H,WANG Y,et al.The effect of anterior projection of aneurysm dome on the rupture of anterior communicating artery aneurysms compared with posterior projection[J].Clin Neurol Neurosurg,2016,143:99-103.
[10] FANG S,BRINJIKJI W,MURAD M H,et al.Endovascular treatment of anterior communicating artery aneurysms:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].AJNR Am J neuroradiol,2014,35(5):943-947.
[11] 陈委,叶宇,欧阳锡华,等.前交通动脉破裂微小动脉瘤的血管内治疗[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2016,19(6):41-43.
[12] FAN L,TAN X,XIONG Y,et al.Stent-assisted coiling versus coiling alone of ruptured anterior communicating artery aneurysms:A single-center experience[J].Clini Neurol Neurosurg,2016,144:96-100.
[13] ITO H,MORISHIMA H,ONODERA H,et al.Acute phase endovascular intervention on a pseudoaneurysm formed due to rupture of an anterior communicating artery aneurysm[J].BMJ Case Rep,2014,2014:bcr2013011006.
[14] SEKHAR L N,NATARAJAN S K,BRITZ G W,et al.Microsurgical management of anterior communicating artery aneurysms[J].Neurosurgery,2007,61:273-290,discussion 290-292.
[15] TARULLI E,SNEADE M,CLARKE A,et al.Effects of circle of Willis anatomic variations on angiographic and clinical outcomes of coiled anterior communicating artery aneurysms[J].AJNR.AmJ neuroradiol,2014,35(8):1 551-1 555.
[16] CAI W,SHI D,GONG J,et al.Are Morphologic Parameters Actually Correlated with the Rupture Status of Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms[J].World Neurosurg,2015,84(5):1 278-1 283.
[17] XIA N,LIU Y,ZHONG M,et al.Smoking Associated with Increased Aneurysm Size in Patients with Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms[J].World Neurosurg,2016,87:155-161.
[18] HU P,QIAN Y,LEE C J,et al.The energy loss may predict rupture risks of anterior communicating aneurysms:a preliminary result[J].International journal of clinical and experimental medicine,2015,8(3):4 128-4 133.
[19] LEE K,SHIN S Y,PARK S H.Acute Retrobulbar Optic Neuropathy as the Sole Manifestation of Subarachnoid Haemorrhage from a Ruptured Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm[J].Neuroophthalmology,2013,37(4):172-174.
[20] CHERIAN M P,PRANESH M B,MEHTA P,et al.Outcomes of endovascular coiling of anterior communicating artery aneurysms in the early post-rupture period:a prospective analysis[J].Neurology India,2011,59(2):218-223.
[21] KIM S,KANG M,CHOI J H,et al.Safety of coil occlusion of the parent artery for endovascular treatment of anterior communicating artery aneurysm[J].Neuroradiol J,2016,29(3):201-207.
[22] LECLERC X,NAVEZ J F,GAUVRIT J Y,et al.Aneurysms of the anterior communicating artery treated with Guglielmi detachable coils:follow-up with contrast-enhanced MR angiography[J].AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002,23:1 121-1 127.
[23] CHIU W T,HONG C T,CHI N F,et al.The risk of intravenous thrombolysis-induced intracranial hemorrhage in Taiwanese patients with unruptured intracra-nial aneurysm[J].PLoS One,2017,12(6):e0180021.
[24] CONNOLLY E S J R,RABINSTEIN A A,CARHUAPOMA J R,et al.Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage:a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association[J].Stroke,2012,43:1 711-1 737.
[25] ZUOQ,YANG P,LVN,et al.Safety of coiling with stent placement for the treatment of ruptured wide-necked intracranial aneurysms:a contemporary cohort study in a high-volume center after improvement of skills and strategy[J].J Neurosurg,2018,17:1-7.
[26] JOHNSON AK,MUNICH SA,HEIFERMAN DM,et al.Stent assisted embo-lization of 64 anterior communicating artery aneurysms[J].J NeurointervSurg,2012,3(Suppl):iii62-iii65.
[27] KOCUR D,SLUSARCZYK W,PRZYBYLKO N,et al.Stent-Assisted Endovascular Treatment of Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms-Literature Review[J].Pol J Radiol,2016,81:374-379.
[28] KOCUR D,ZBROSZCZYK M,PRZYBYLKO N,et al.Stent-assisted embolization of wide-neck anterior communicating artery aneurysms:Review of consecutive 34 cases[J].Neurol NeurochirPol,2016,50(6):425-431.
[29] 蔡可夫,周宏智.颅内前交通宽颈动脉瘤的血管内介入治疗[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2012,15(22):46-47.
[30] GUEST W,SARMA D,MAROTTA T.Partial thrombosis of an anterior communicating artery aneurysm prior to endovascular coiling,with intra-procedural distal thrombus embolization[J].Interv Neuroradiol,2017,23(6):589-593.
[31] KASUYA H,SHIMIZU T,NAKAYA K,et al.Angles between A1 and A2 segments of the anterior cerebral artery visualized by three-dimensional computed tomographic angiography and association of anterior communicating artery aneurysms[J].Neurosurgery,1999,45(1):89-93.
[32] LI J W,SHI C H.Endovascular treatment of compli-cated ruptured anterior communicating artery aneury-sms based on the anatomical features of the anterior communicating artery complex[J].Neurol India,2012,60(1):55-60.
[33] HUANG Q H,WU Y F,XU Y,et al.Vascular geometry change because of endovascular stent placement for anterior communicating artery aneurysms[J].A JNR Am J Neuroradiol,2011,32(9):1 721-1 725.
[34] HO M J,GRICKE S L,MUMMEL P,et al.Stent-Assisted Treatment of Ruptured Intracranial Aneury-sms in the Acute Phase:A Single Center Experience[J].Neurol Sci,2018(10):31-36.
[35] MCLAUGHLIN N,MCARTHUR D L,MARTIN N A.Use of stent-assisted coil embolization for the treatment of wide-necked aneurysms:A systematic review[J].Surg Neurol Int,2013,4:43.
[36] KIM M C,HWANG S K.The Rupture Risk of Aneurysm in the Anterior Communicating Artery:A Single Center Study[J].J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg,2017,19(1):36-43.
[37] LIANG F,LIU X,YAMAGUCHI R,et al.Sensitivity of flow patterns in aneurysms on the anterior communicating artery to anatomic variations of the cerebral arterial network[J].J Biomech,2016,49(15):3 731-3 740.
[38] SHIMIZU T,NAITO I,AIHARA M,et al.Visual outcomes of endovascular and microsurgical treatment for large or giant paraclinoid aneurysms[J].Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2015,157:13-20.
[39] XIAOYING Z,XICAI C,SHENG L.Management for the case of twice ruptured anterior communicating artery aneurysm:from nursing perspective[J].J Vasc Nurs,2013,31(3):107-110.
(收稿2018-09-09 修回2018-10-09)
本文责编:关慧
本文引用信息:程哲,闵敬亮,杨光,张辉,王昊,来汉生.血管内介入治疗破裂前交通动脉瘤的疗效分析[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2018,21(21):2331-2337.DOI:10.12083/SYSJ.2018.21.501
Reference information:CHENG Zhe,MIN Jingliang,YANG Guang,ZHANG Hui,WANG Hao,LAI Hansheng.Efficacy analysis of endovascular interventional treatment for ruptured anterior communicating artery aneurysms[J].Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases,2018,21(21):2331-2337.DOI:10.12083/SYSJ.2018.21.501